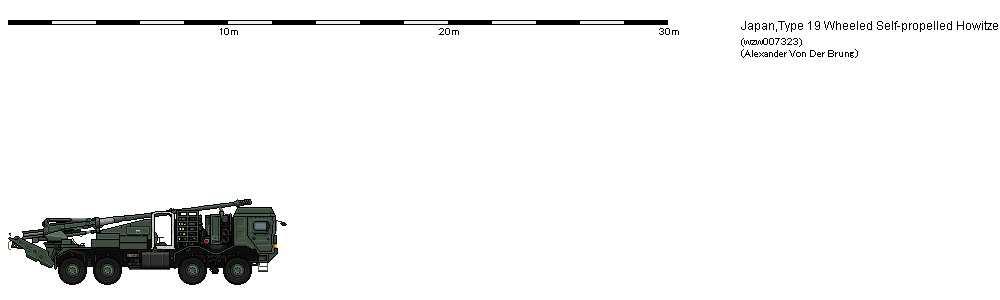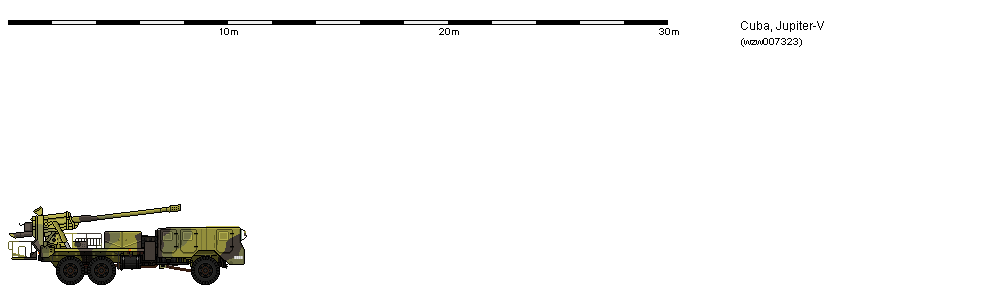
FD scale Vehicles 13
Moderator: Community Manager
Re: FD scale Vehicles 13
Some ww2 french hippo
Fourgon Modele 1887

Chariot Modele 1874-1901

Fourgon Modele 1887

Chariot Modele 1874-1901

Re: FD scale Vehicles 13
Excellent!
Great to see You back with new works!
Great to see You back with new works!
Re: FD scale Vehicles 13
Germany, GTK Boxer A1 Führungsfahrzeug


Last edited by odendasf on May 21st, 2024, 4:05 am, edited 1 time in total.
- darthpanda
- Posts: 3429
- Joined: July 28th, 2010, 2:14 pm
- Location: HOLLAND!!!!!!!
- Contact:
Re: FD scale Vehicles 13
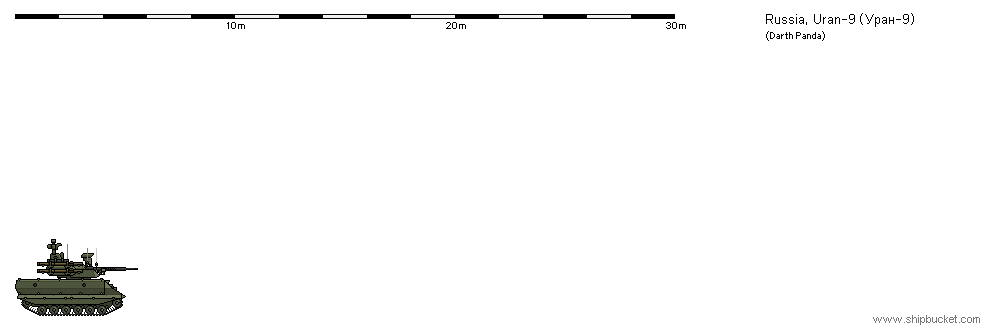
Russia - Uran-9

Re: FD scale Vehicles 13
Vickers Light Tank Mk.VI
Suprisingly overlooked, the Light Tank Mk.VI was the most numerous British tank type at the beginning of WWII.

The Mk.VI was the ultimate model of Vickers interwar light tank family, being an updated version of the previous Mk.IV.
Production started in 1936 of what was seen as the best light tank in the world. As with almost all designs initial service revealed some teething troubles, and after less than 50 had been built poduction shifted to the Mk.VIA. The track return roller was relocated rearwards from the front bogie, while the turret was reshaped and the commander's cupola changed (each model of the Mk.VI would be made with a different cuploa). The initial batch were relegated to training duties.
The Mk.VIB followed, with the design being simplified for mass production and the armour thickened. Production was also undertaken in India, these vehicles being Mk.IVB India pattern. This model had the cupola replaced by a periscope.
The final Mk.VIC also had the commander's periscope, and now sported a larger BESA gun.
Over 1000 were in service at the start of WWII, and MK.VI's of all versions were the major tank component of the BEF before the fall of France, where large numbers were abandoned. But the Mk.VI saw its best service in North Africa, Malta and the Middle East where they performed well against the Italians, and in Syria and Iran. By 1942 they were phased out with the arrival of the M3 Stuart.
After the Fall of France, the Mk.VI was proposed as the basis for an anti-aircraft tank to defend armoured columns. Two prototypes of a Light AA Tank were modified from Mk.VI's. The second prototype was built from an early Mk.VI hull with a aircraft Boulton-Paul type A turret. It was soon realised that the glazing was unneccessary in a vehicle and was removed.
From this the initial Light AA Tank Mk.I entered production. Built on Mk.VIA or VIB hulls, modified vehicles were fitted with a new raised box hull and four light machine guns. Production then switched to the Light AA Tank Mk.II, fitted with a revised electric turret, lowered casement to lower the centre of gravity, and an external ammunition bin. About 50 vehicles were converted.
Suprisingly overlooked, the Light Tank Mk.VI was the most numerous British tank type at the beginning of WWII.

The Mk.VI was the ultimate model of Vickers interwar light tank family, being an updated version of the previous Mk.IV.
Production started in 1936 of what was seen as the best light tank in the world. As with almost all designs initial service revealed some teething troubles, and after less than 50 had been built poduction shifted to the Mk.VIA. The track return roller was relocated rearwards from the front bogie, while the turret was reshaped and the commander's cupola changed (each model of the Mk.VI would be made with a different cuploa). The initial batch were relegated to training duties.
The Mk.VIB followed, with the design being simplified for mass production and the armour thickened. Production was also undertaken in India, these vehicles being Mk.IVB India pattern. This model had the cupola replaced by a periscope.
The final Mk.VIC also had the commander's periscope, and now sported a larger BESA gun.
Over 1000 were in service at the start of WWII, and MK.VI's of all versions were the major tank component of the BEF before the fall of France, where large numbers were abandoned. But the Mk.VI saw its best service in North Africa, Malta and the Middle East where they performed well against the Italians, and in Syria and Iran. By 1942 they were phased out with the arrival of the M3 Stuart.
After the Fall of France, the Mk.VI was proposed as the basis for an anti-aircraft tank to defend armoured columns. Two prototypes of a Light AA Tank were modified from Mk.VI's. The second prototype was built from an early Mk.VI hull with a aircraft Boulton-Paul type A turret. It was soon realised that the glazing was unneccessary in a vehicle and was removed.
From this the initial Light AA Tank Mk.I entered production. Built on Mk.VIA or VIB hulls, modified vehicles were fitted with a new raised box hull and four light machine guns. Production then switched to the Light AA Tank Mk.II, fitted with a revised electric turret, lowered casement to lower the centre of gravity, and an external ammunition bin. About 50 vehicles were converted.
Re: FD scale Vehicles 13
Auto Mitrailleuse de Combat
AMC Schneider P16 / AMC Citroën-Kégresse modèle 1929 / Schneider-Kegresse P16 modèle 29

AMC Schneider P16 / AMC Citroën-Kégresse modèle 1929 / Schneider-Kegresse P16 modèle 29

Re: FD scale Vehicles 13
Vickers Light Tank Mk.VI in German service
In the aftermath of the evacuation of the BEF, the British army left almost all of its equipment behind in France. The tank crews did their best to permanently disable their vehicles, but the Germans were able to resurrect some.

The captured Mk.VIB and Mk.VIC's now became Leichter Panzerkampfwagen Mk.VIB 735(e) and Leichter Panzerkampfwagen Mk.VIC 736(e) in German service. They were however no longer suitable for frontline combat duties, and found themselves relegated to training and policing duties.
Six vehicles were modified to become self-propelled field guns, fitted with the WWI vintage 10.5cm leFH 16 howitzer. The mobile guns were used in coastal defence in France until Barbarosa, when they were sent to support Gerrman troops near Leningrad. By March 1942 all vehicles had been destroyed, but they had prooved the validity of the concept, and other, larger vehicles were later similarly modified.
In the aftermath of the evacuation of the BEF, the British army left almost all of its equipment behind in France. The tank crews did their best to permanently disable their vehicles, but the Germans were able to resurrect some.

The captured Mk.VIB and Mk.VIC's now became Leichter Panzerkampfwagen Mk.VIB 735(e) and Leichter Panzerkampfwagen Mk.VIC 736(e) in German service. They were however no longer suitable for frontline combat duties, and found themselves relegated to training and policing duties.
Six vehicles were modified to become self-propelled field guns, fitted with the WWI vintage 10.5cm leFH 16 howitzer. The mobile guns were used in coastal defence in France until Barbarosa, when they were sent to support Gerrman troops near Leningrad. By March 1942 all vehicles had been destroyed, but they had prooved the validity of the concept, and other, larger vehicles were later similarly modified.