Difference between revisions of "ET 1913 g Novaya Verf Brilliant class destroyer"
| Line 51: | Line 51: | ||
==Development== | ==Development== | ||
| − | After the defeat in Far Eastern - Japanese war, the war experience and lessons were theraly analysed in the "Special committee of readjustment in naval affairs" which was formed after the humiliating defeat in the Tsusima straight. One of the main lessons of the war regarding torpedo ships were, that destroyers were far more versatile than just aggressive torpedo attackers. They performed vast range of different naval missions and thus the new requirement for future destroyers emphasized multipurpose capability. New type of destroyers were to operate in higher speeds and longer range with better sea keeping capabilities. This in return meant that the future destroyers would be considerably larger than the earlier ones. Novaya Verf build prototype ship for these new requirements called Oniks and after analyzing the performance of the new ship, a tender for total of 27 new destroyers were issued upon three shipyards; Novaya Verf in Dalny, Dalzavod in Vladivostok and Amurskiy Sudostroitelnyy Zavod in | + | After the defeat in Far Eastern - Japanese war, the war experience and lessons were theraly analysed in the "Special committee of readjustment in naval affairs" which was formed after the humiliating defeat in the Tsusima straight. One of the main lessons of the war regarding torpedo ships were, that destroyers were far more versatile than just aggressive torpedo attackers. They performed vast range of different naval missions and thus the new requirement for future destroyers emphasized multipurpose capability. New type of destroyers were to operate in higher speeds and longer range with better sea keeping capabilities. This in return meant that the future destroyers would be considerably larger than the earlier ones. Novaya Verf build prototype ship for these new requirements called Oniks and after analyzing the performance of the new ship, a tender for total of 27 new destroyers were issued upon three shipyards; Novaya Verf in Dalny, Dalzavod in Vladivostok and Amurskiy Sudostroitelnyy Zavod in Permskoye-na-Amure. Each shipyard were given set of design requirements but other than that, each company was responsible of designing their boats. It resulted 3 different group of relatively similar performance destroyers. |
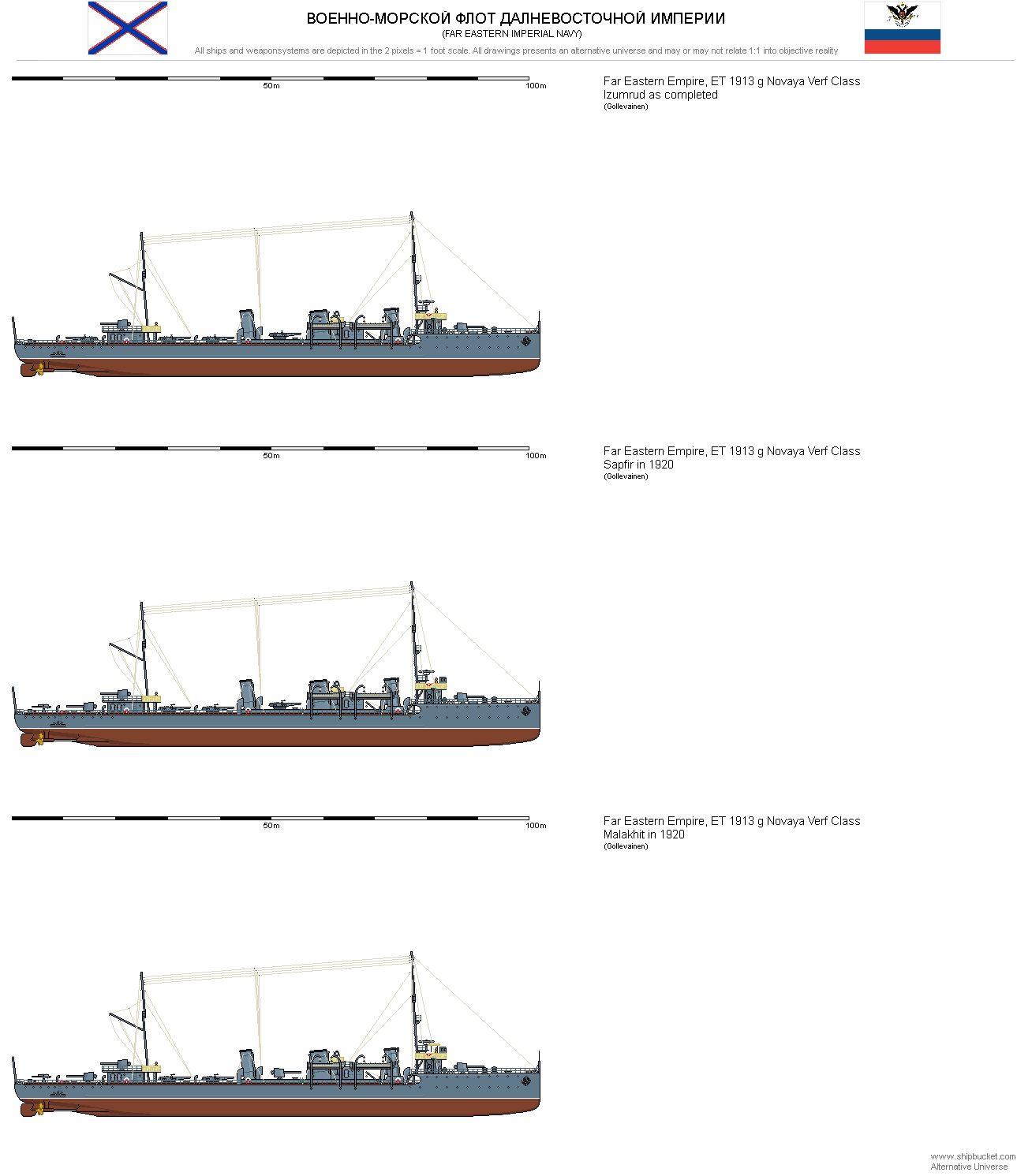
Novaya Verf's design was based on the earlier Oniks but had some differences according to the new design parameters. The short forecastle with the break was replaced with longer one and the bridge structure was placed above the forecastle deck. Ships carried 2 new 120mm/45 guns and 4 set of twin torpedo tubes. Later units of the class had one or two of the twin torpedo tubes replaced with additional 120mm guns. The boats had two-shaft machinery and only 4 boilers compared 6 to the Oniks class but with increased capacity and thus still making 37,000 hp. Initially the machinery was to be brought from Germany as it was the case with the Oniks class. However after the start of the First World War, German turbines were no longer available. Only the first 3 units received their original machinery. The remainder had indigenous machinery set which prolonged their construction considerably. | Novaya Verf's design was based on the earlier Oniks but had some differences according to the new design parameters. The short forecastle with the break was replaced with longer one and the bridge structure was placed above the forecastle deck. Ships carried 2 new 120mm/45 guns and 4 set of twin torpedo tubes. Later units of the class had one or two of the twin torpedo tubes replaced with additional 120mm guns. The boats had two-shaft machinery and only 4 boilers compared 6 to the Oniks class but with increased capacity and thus still making 37,000 hp. Initially the machinery was to be brought from Germany as it was the case with the Oniks class. However after the start of the First World War, German turbines were no longer available. Only the first 3 units received their original machinery. The remainder had indigenous machinery set which prolonged their construction considerably. | ||
Revision as of 10:47, 7 April 2020
| ET 1913 g Novaya Verf Brilliant class Destroyer | |
|---|---|
| Class overview | |
| Name | ET 1913 g Novaya Verf Brilliant class Destroyer |
| Operators | Far Eastern Imperial Navy |
| Class before | ET 1910 g Oniks class destroyer |
| Planned | 9 |
| Built | 9 |
| Active | 9 |
| General Characteristics | |
| Type | Destroyer |
| Displacement |
|
| Length | 102.4 metres (336 ft) |
| Beam | 9.5 metres (31 ft) |
| Draught | 3.53 metres (11.6 ft) |
| Propulsion | 2 shafts, 2 AEG-Vulkan Steam turbines (see notes) |
| Power |
|
| Speed | 34 kts |
| Range | 2600 nm at 21 kts |
| Complement | 122 |
| Armament |
|
Development
After the defeat in Far Eastern - Japanese war, the war experience and lessons were theraly analysed in the "Special committee of readjustment in naval affairs" which was formed after the humiliating defeat in the Tsusima straight. One of the main lessons of the war regarding torpedo ships were, that destroyers were far more versatile than just aggressive torpedo attackers. They performed vast range of different naval missions and thus the new requirement for future destroyers emphasized multipurpose capability. New type of destroyers were to operate in higher speeds and longer range with better sea keeping capabilities. This in return meant that the future destroyers would be considerably larger than the earlier ones. Novaya Verf build prototype ship for these new requirements called Oniks and after analyzing the performance of the new ship, a tender for total of 27 new destroyers were issued upon three shipyards; Novaya Verf in Dalny, Dalzavod in Vladivostok and Amurskiy Sudostroitelnyy Zavod in Permskoye-na-Amure. Each shipyard were given set of design requirements but other than that, each company was responsible of designing their boats. It resulted 3 different group of relatively similar performance destroyers.
Novaya Verf's design was based on the earlier Oniks but had some differences according to the new design parameters. The short forecastle with the break was replaced with longer one and the bridge structure was placed above the forecastle deck. Ships carried 2 new 120mm/45 guns and 4 set of twin torpedo tubes. Later units of the class had one or two of the twin torpedo tubes replaced with additional 120mm guns. The boats had two-shaft machinery and only 4 boilers compared 6 to the Oniks class but with increased capacity and thus still making 37,000 hp. Initially the machinery was to be brought from Germany as it was the case with the Oniks class. However after the start of the First World War, German turbines were no longer available. Only the first 3 units received their original machinery. The remainder had indigenous machinery set which prolonged their construction considerably.
Ships in class
| Name | Builder | Laid down | Launch Date | Entered Service | Fate |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Brilliant | Novaya Verf, Dalny | July 1913 | June 1914 | November 1915 | Extant in 1920 |
| Izumrud | Novaya Verf, Dalny | July 1913 | June 1914 | November 1915 | Extant in 1920 |
| Ametist | Novaya Verf, Dalny | July 1913 | June 1914 | December 1915 | Extant in 1920 |
| Sapfir | Novaya Verf, Dalny | May 1914 | August 1915 | December 1916 | Extant in 1920 |
| Zhemchug | Novaya Verf, Dalny | May 1914 | August 1915 | December 1917 | Extant in 1920 |
| Rubin | Novaya Verf, Dalny | May 1914 | August 1915 | January 1918 | Extant in 1920 |
| Bazalt | Novaya Verf, Dalny | July 1915 | October 1917 | June 1919 | Extant in 1920 |
| Granat | Novaya Verf, Dalny | July 1915 | October 1917 | July 1919 | Extant in 1920 |
| Malakhit | Novaya Verf, Dalny | July 1915 | October 1917 | August 1919 | Extant in 1920 |